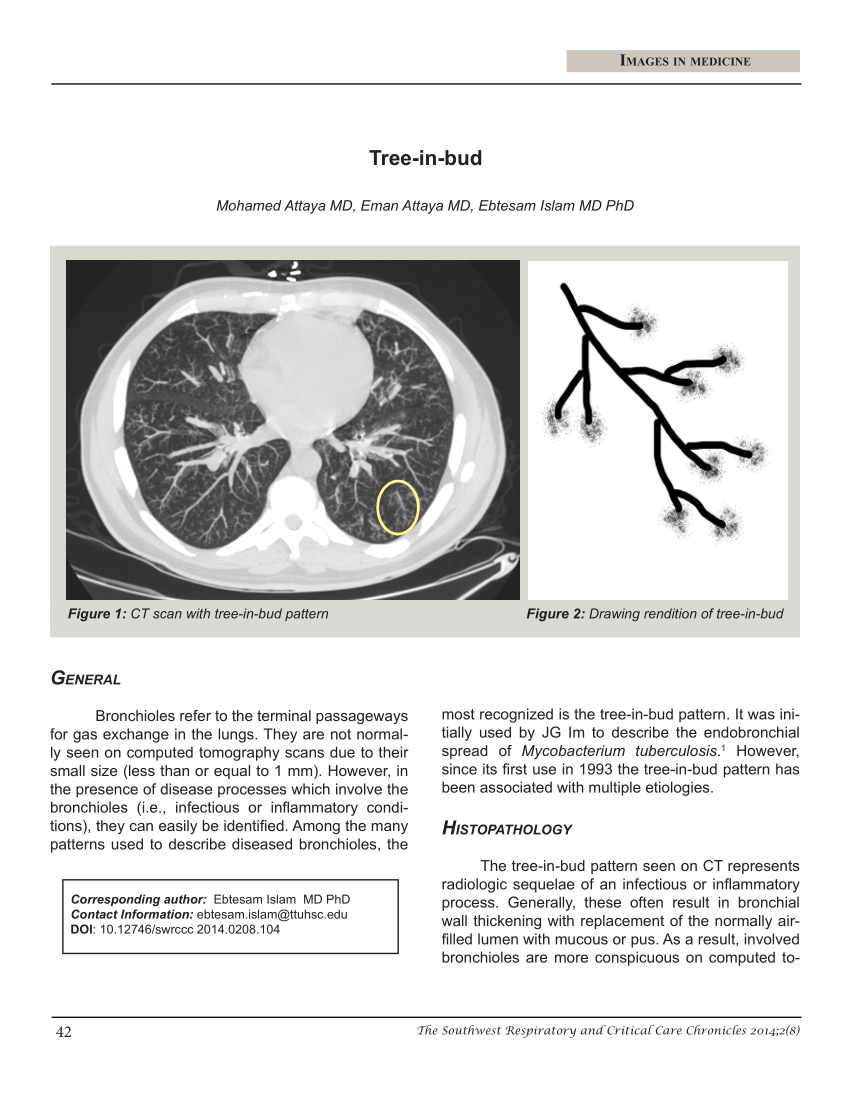
tree in bud opacities seen in
The differential with superimposed infection should be considered septal thickening may occur later with the alveolar opacities producing a crazy paving pattern 6. It is a non-specific sign with a wide etiology including infection chronic interstitial disease and acute alveolar disease.
Tend to resolve or coalesce tree-in-bud appearances.

. Because of the wide variability in the disease process presenting complaints will vary. Small patchy peripheral opacities are also present in the left lower lobe. The clinical and CT findings of numerous respiratory viral pathogens such as influenza human parainfluenza virus HPIV respiratory syncytial virus RSV rhinovirus and adenovirus have been described 12RSV shows an airway-centric pattern of disease with tree-in-bud opacity and bronchial wall thickening.
Additional features that are sometimes seen include 16. In the remaining 67 273 of. High-resolution CT scan of the thorax demonstrates central bronchiectasis a hallmark of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis right arrow and the peripheral tree-in-bud appearance of centrilobular opacities left arrow which represent mucoid impaction of the small bronchioles.
However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. Ground-glass opacificationopacity GGO is a descriptive term referring to an area of increased attenuation in the lung on computed tomography CT with preserved bronchial and vascular markings. Chest CT showed a filling defect in the left atrium and a mobile left atrial mass was seen on transthoracic echocardiography shown in a.
A 47-year-old woman presented with shortness of breath. Chronic Kerley B lines may be caused by fibrosis or hemosiderin deposition caused by recurrent pulmonary edema. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
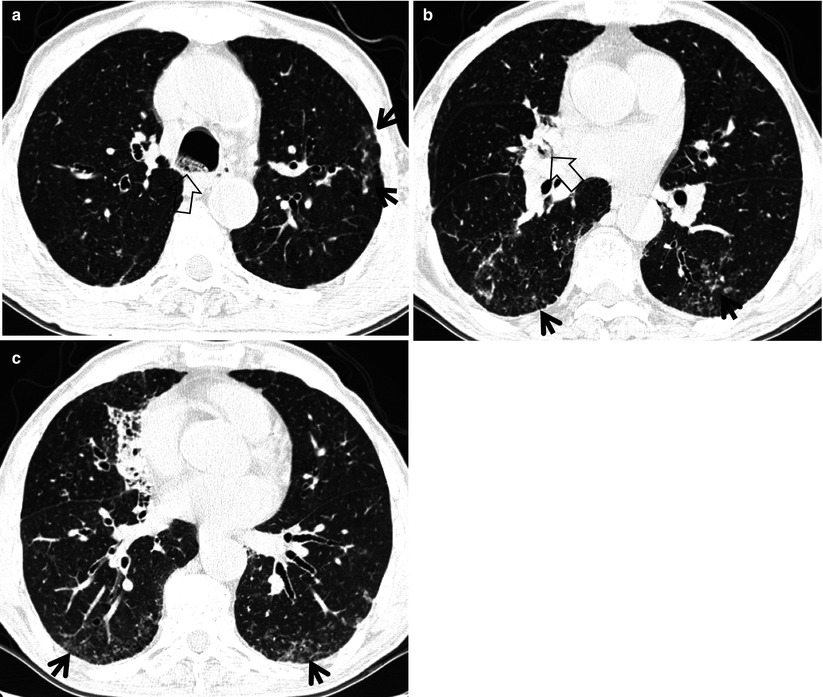
Adnexal or orbital disease may be seen with preauricular lymphadenopathy. TIB opacities were seen in association with bronchiectasis in 30 123 of 406 of cases and with an apical-predominant disease in 25 10 of 406 cases. In the right mid-lung nodular opacities are in a tree-in-bud distribution suggestive of endobronchial.
They are suggestive for the diagnosis of congestive heart failure but are also seen in various non-cardiac conditions such as pulmonary fibrosis interstitial deposition of heavy metal particles or carcinomatosis of the lung.
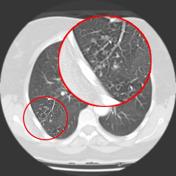
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

Tree In Bud Caused By Haemophilus Influenzae Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad
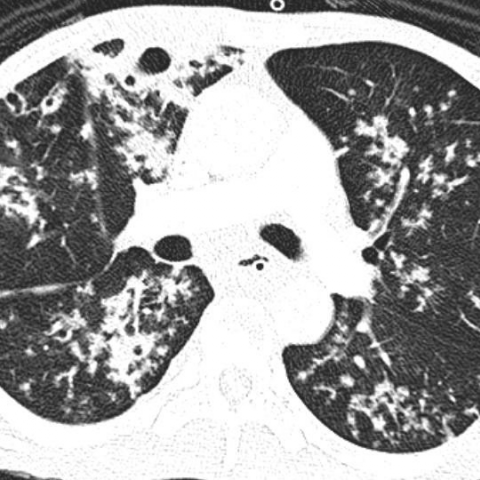
Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad

Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Tree In Bud Pattern Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Pdf Tree In Bud Semantic Scholar

Computed Tomography Of The Chest Showed Nodular Opacities With Tree In Download Scientific Diagram

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad

Hrct Scan Of The Chest Showing Diffuse Micronodules And Tree In Bud Download Scientific Diagram